What is Botulinum toxin or Botox?
Botulinum toxin (more commonly known as Botox) is a protein made by the bacteria Clostridium Botulinum. The type of Botox that is usually used for injections is Type A.
When injected, the toxin disrupts nerve messages to muscles and causes temporary paralysis in that muscle.
It is widely used in medicine for many conditions and has an excellent safety profile.
Why are botulinum toxin injections necessary?
Botulinum toxin injections cause temporary paralysis of muscles around the site of the injections.
This is useful to treat conditions with unwanted contractions of the muscles around the eye. These include blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm.
Botulinum toxin injections work for approximately 90% of people with blepharospasm and generally lasts up to 2 months.
Ok, so what is blepharospasm?
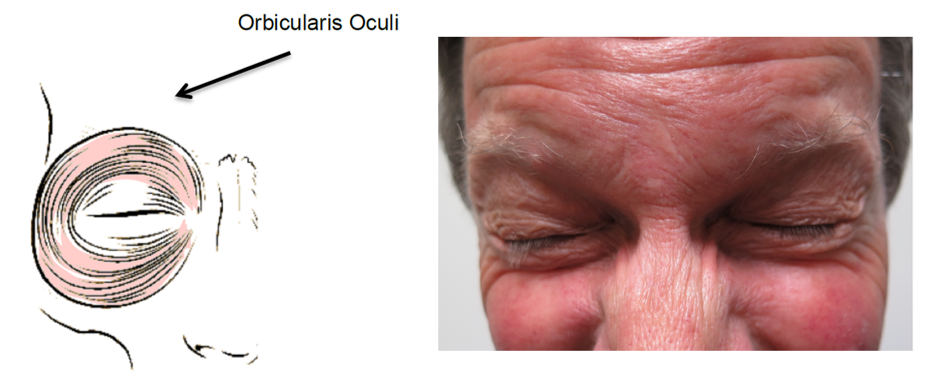
Blepharospasm is a condition where patients experience involuntary and excessive eyelid blinking. This is due to spasms of the orbicularis oculi, which is the muscle that controls blinking.
The exact cause of blepharospasm is unknown. Sometimes blepharospasm has a known cause, such as dry and irritated eyes, or stress.
Symptoms include involuntary blinking which are usually mild and occasional initially, but become more severe and frequent over time. Patients might even experience spasms of their face and neck.
Most patients have symptoms on both sides, but some are affected mainly on one side.
There may be triggers for the spasms, such as bright light. Spasms may decrease when sleeping or when concentrating on a specific task.
What does botulinum toxin injection involve?
Botox is usually injected into the orbicularis oculi muscle or sometimes into the eyelid itself. The amount required for symptom improvement varies between patients.
At each session, multiple different areas of the orbicularis muscle are injected to maximize the effect. Injections are given both above and below the eye. You will receive between 4 to 8 injection points around each eye.
The ideal amount for each patient will take a few treatments to determine. This is because the response can vary between visits, even when injecting the same total amount of toxin.
What are the potential risks?
Botulinum toxin has been used safely for over 20 years. There are no known long term side effects or diseases caused by the use of botulinum toxin.
Short-term side effects include:
● Bleeding and bruising around the injection site● Headache (occurs in 10%)
● Drooping of the eyelids (occurs in up to 7%)
● Dry eye symptoms requiring treatment with lubricating eye drops
● Allergic reaction – this is very rare and requires emergency treatment
Longer-term side effects (up to 2 months until the effects wear off) include:
● Paralysis of the orbicularis muscle causing inability to close the eyes● Excessive drooping of the eyelids
● Double vision
See Related: Surgical treatment of droopy eyelids (ptosis)
When should I not have botulinum toxin injections?
You should not receive injections if you have an allergy to any component of the preparation.
If you have active infectious conjunctivitis, you should not receive injections until the infection has resolved.
If you have any concern over whether or not botulinum toxin is suitable for you, please discuss it with your treating ophthalmologist.
Circumstances such as pregnancy and breast-feeding must be decided upon on a case-by-case basis
What can I expect?
Before injection
The injections can be a little painful, but most patients tolerate them well. The skin can be cooled prior with an icepack to make the skin a little numb before injection.
During injection
The toxin is injected with fine needles in small amounts, slowly, to minimize pain. The procedure is usually relatively painless.
Generally, multiple injections are given both above and below the eye. Anywhere from 4-8 injection points around each eye may be done.
After injection
It takes between one and four days for the paralysis to begin. The complete effect usually sets in at one week. The treatment often lasts up to three months, although the effect has been reported to last up to six months.
The timing of repeat injections will depend on the individual. After many months of treatment, you may find that the injections need to be given slightly more frequently.
You can continue your day as you normally would after the injections. You may shower, bathe or apply makeup afterwards. Normal facial expressions and activities such as reading or watching television, are perfectly ok.
It is advisable not to partake in strenuous exercise, or have a massage or facial for at least 24 hours after the injection because this can increase the risk of eyelid droop.
What if the injections do not work?
If Botox stops working or is ineffective, surgery is usually the preferred treatment. The procedure performed is called a myectomy, and involves removal of some of muscles around the eyelid.
This procedure is usually effective in up to 85% of cases. The amount of muscle removed will be decided by your surgeon and differs between patients.
See Related: What to expect when having your eyelid droop repaired


